A diabetic diet, often referred to as Medical Nutrition Therapy (MNT) for diabetes, is a structured eating plan designed to help individuals manage their blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes. This diet is tailored to meet the unique needs of each person, taking into account factors such as age, sex, physical activity level, and the type of diabetes they have. Let’s delve into the specifics of what constitutes a diabetic diet and how it can be effectively implemented.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Dietary Requirements
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational Diabetes. Regardless of the type, managing blood sugar levels is crucial to preventing complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. A well-structured diabetic diet plays a pivotal role in achieving this goal.
Key Components of a Diabetic Diet
1. Carbohydrate Management
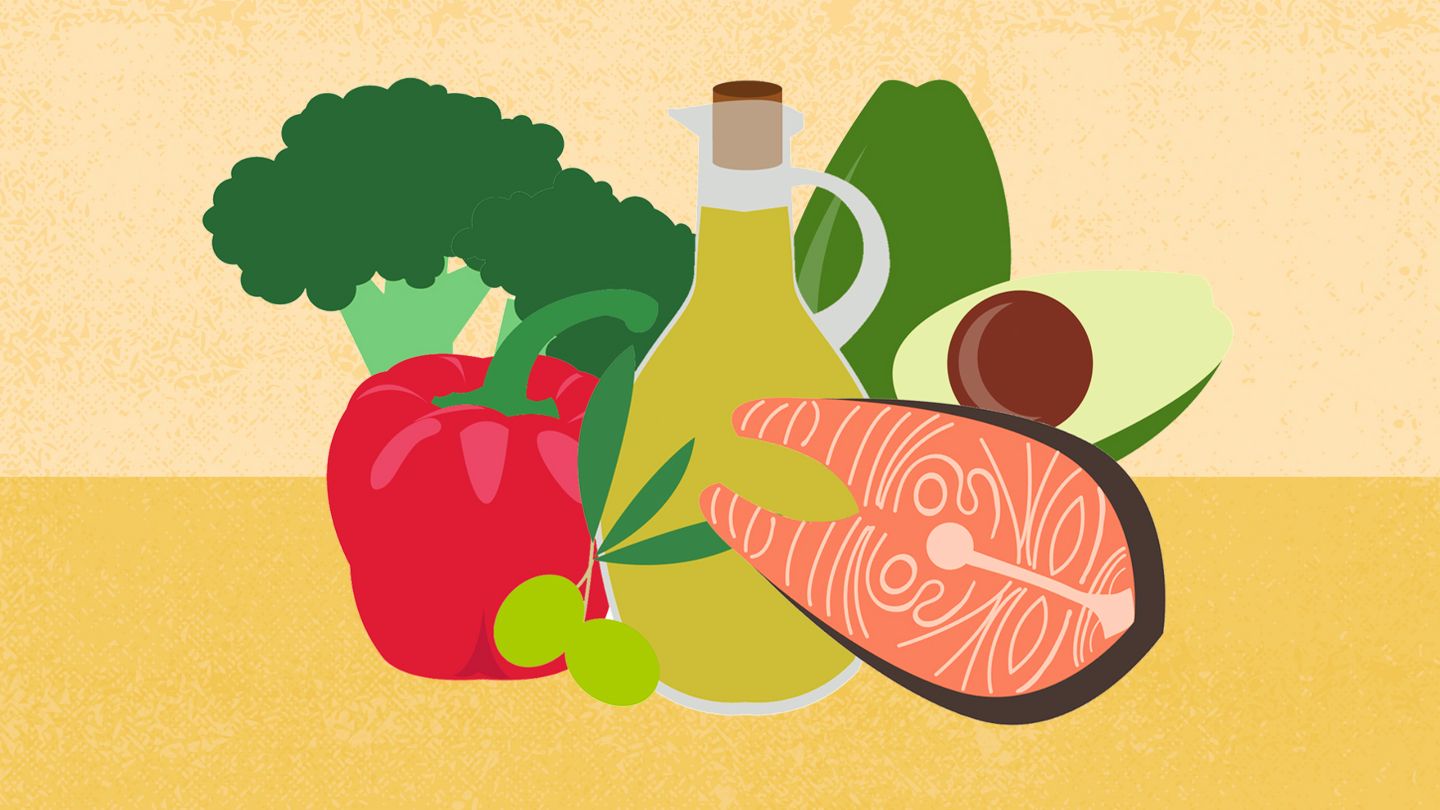
Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels. Therefore, managing carbohydrate intake is essential for individuals with diabetes. The focus is on consuming complex carbohydrates found in whole grains, vegetables, legumes, and fruits, which provide a steady release of glucose into the bloodstream.
a. Whole Grains: Foods such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread are rich in fiber and have a lower glycemic index, making them ideal for a diabetic diet.
b. Vegetables: Non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and peppers are low in carbohydrates and high in essential vitamins and minerals.
c. Fruits: While fruits contain natural sugars, they also provide fiber, which helps moderate blood sugar spikes. Opt for whole fruits over fruit juices.
2. Protein Intake
Protein is a crucial component of a diabetic diet as it helps with satiety and stabilizes blood sugar levels. Sources of lean protein include:
a. Fish: Particularly fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, which are high in omega-3 fatty acids.
b. Poultry: Skinless chicken and turkey are excellent choices.
c. Plant-Based Proteins: Beans, lentils, and tofu provide plant-based protein and fiber.
3. Healthy Fats
Incorporating healthy fats into the diet is important for overall health and can help in managing blood sugar levels. Sources of healthy fats include:
a. Avocado: Rich in monounsaturated fats, which are beneficial for heart health.
b. Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are excellent sources of healthy fats and fiber.
c. Olive Oil: A staple of the Mediterranean diet, known for its numerous health benefits.

Meal Planning and Portion Control
Proper meal planning and portion control are vital aspects of a diabetic diet. Here are some strategies to ensure effective management of food intake:
a. Plate Method: This involves dividing the plate into sections to ensure a balanced meal. Half the plate should consist of non-starchy vegetables, a quarter should be lean protein, and the remaining quarter should be whole grains or starchy vegetables.
b. Counting Carbohydrates: This technique helps in keeping track of the amount of carbohydrates consumed during meals and snacks. It is particularly useful for individuals on insulin therapy.
c. Glycemic Index (GI): Choosing foods with a low glycemic index can help in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. The GI measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels.
Hydration and Beverage Choices
Staying hydrated is essential, and beverage choices can significantly impact blood sugar levels. The best options include:
a. Water: The ideal choice for hydration.
b. Herbal Teas: Unsweetened herbal teas provide hydration without affecting blood sugar levels.
c. Coffee: Plain coffee without added sugars or high-fat creamers can be consumed in moderation.
Special Considerations for Different Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
For individuals with Type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is necessary. The diet must be meticulously planned to balance carbohydrate intake with insulin doses to prevent hypo- or hyperglycemia. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is critical.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is often managed through diet, exercise, and oral medications. The focus is on weight management and improving insulin sensitivity through a balanced diet rich in fiber and low in refined sugars.
Gestational Diabetes
Pregnant women with gestational diabetes need to follow a diet that supports healthy fetal development while managing blood sugar levels. This includes small, frequent meals and snacks to prevent blood sugar spikes and ensure adequate nutrition.
The Role of Physical Activity
Combining a diabetic diet with regular physical activity enhances blood sugar control and overall health. Exercise helps the body use insulin more efficiently and lowers blood sugar levels. Activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling are highly beneficial.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals
It’s essential to work with healthcare professionals, including dietitians and diabetes educators, to create a personalized diabetic diet plan. They can guide meal planning, portion sizes, and adjusting the diet based on individual needs and medical conditions.
Conclusion.
A diabetic diet, or Medical Nutrition Therapy (MNT), is a personalized eating plan designed to help individuals manage their blood sugar levels effectively. By focusing on balanced meals that include complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats, individuals with diabetes can maintain stable blood sugar levels and improve their overall health. Proper meal planning, portion control, and hydration are key components of this diet. Additionally, regular physical activity and consultation with healthcare professionals are essential for optimal diabetes management.