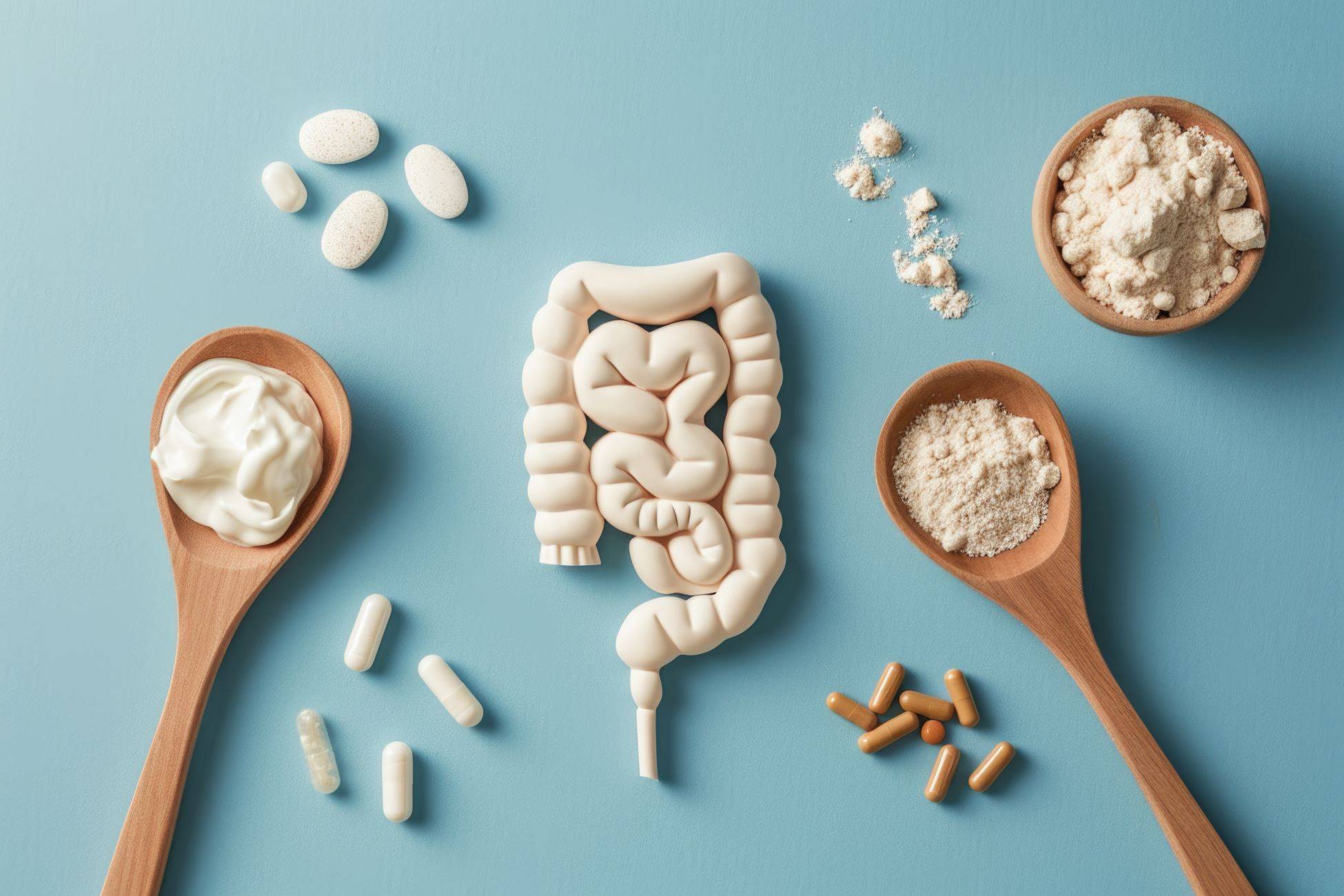
Probiotics are live microorganisms that provide numerous health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. They play a crucial role in maintaining gut health, boosting the immune system, and even influencing mental well-being. With the growing popularity of probiotics, it is essential to understand what makes a good probiotic and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Understanding Probiotics
Probiotics are often referred to as “good” or “friendly” bacteria because they help balance the gut microbiome, which is essential for overall health. These beneficial bacteria can be found in various fermented foods and dietary supplements. The most common types of probiotics include Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Saccharomyces boulardii.
Lactobacillus
Lactobacillus is a type of bacteria found in the digestive, urinary, and genital systems. It is commonly present in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut. Lactobacillus strains are known for their ability to produce lactic acid, which helps inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria in the gut.
Bifidobacterium
Bifidobacterium is another essential group of bacteria found in the intestines. These bacteria are crucial for breaking down dietary fiber, supporting the immune system, and preventing infections. Bifidobacterium is commonly found in dairy products and some fermented foods.
Saccharomyces boulardii
Saccharomyces boulardii is a yeast used as a probiotic. It is effective in treating and preventing diarrhea, especially antibiotic-associated diarrhea. This probiotic is available in supplement form and has shown promise in maintaining gut health.
Key Factors in a Good Probiotic
When selecting a probiotic, several factors determine its quality and effectiveness. Here are the key considerations:
Strain Specificity
Not all probiotics are created equal. Different strains of bacteria and yeast offer various health benefits. It is crucial to choose a probiotic with strains that are well-researched and proven to be effective for your specific health concerns. For instance, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG is known for its effectiveness in treating diarrhea, while Bifidobacterium longum helps alleviate irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms.
CFU Count
Colony Forming Units (CFUs) indicate the number of live microorganisms in a probiotic supplement. A good probiotic should have a high CFU count, typically ranging from 1 billion to 100 billion per serving. The appropriate CFU count depends on the specific health condition being addressed. For general health maintenance, a lower CFU count may suffice, while higher counts are often recommended for more severe digestive issues.
Survivability
Probiotics must survive the acidic environment of the stomach to reach the intestines, where they can exert their beneficial effects. Look for probiotics that use advanced delivery systems, such as enteric-coated capsules, which protect the bacteria from stomach acid and ensure they reach the gut alive.
Clinical Evidence
The effectiveness of a probiotic should be backed by scientific research and clinical trials. Reputable brands will provide evidence of their product’s efficacy through published studies. This information can often be found on the company’s website or product packaging.
Storage and Shelf Life
Probiotics are sensitive to heat, light, and moisture. To ensure the viability of the bacteria, choose products that are properly stored and have a long shelf life. Some probiotics require refrigeration, while others are shelf-stable. Always follow the storage instructions provided by the manufacturer.
Additional Ingredients
Check the ingredient list for any additives, fillers, or potential allergens. A good probiotic should have minimal additional ingredients and be free from artificial preservatives, colors, and flavors. It is also essential to ensure that the product does not contain any allergens that may affect you.

Benefits of Probiotics
A good probiotic offers numerous health benefits, including:
Improved Digestive Health
Probiotics help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which is essential for optimal digestion. They can alleviate symptoms of digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and constipation.
Enhanced Immune Function
Probiotics boost the immune system by stimulating the production of antibodies and enhancing the activity of immune cells. Regular consumption of probiotics can reduce the incidence of common infections like the cold and flu.
Mental Health Benefits
Emerging research suggests a strong connection between gut health and mental well-being, known as the gut-brain axis. Probiotics can help reduce symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress by influencing the production of neurotransmitters and reducing inflammation.
Weight Management
Certain probiotic strains may aid in weight management by regulating appetite, reducing fat storage, and improving metabolism. Probiotics can also help prevent obesity-related conditions like metabolic syndrome.
Skin Health
Probiotics can benefit skin health by reducing inflammation and improving conditions such as eczema, acne, and rosacea. They achieve this by balancing the gut microbiome, which in turn affects the skin’s condition.
Conclusion.
A good probiotic can significantly impact your health by improving digestive function, enhancing immune response, and supporting overall well-being. By understanding the key factors that make a probiotic effective and choosing one that meets your specific needs, you can harness the full potential of these beneficial microorganisms.